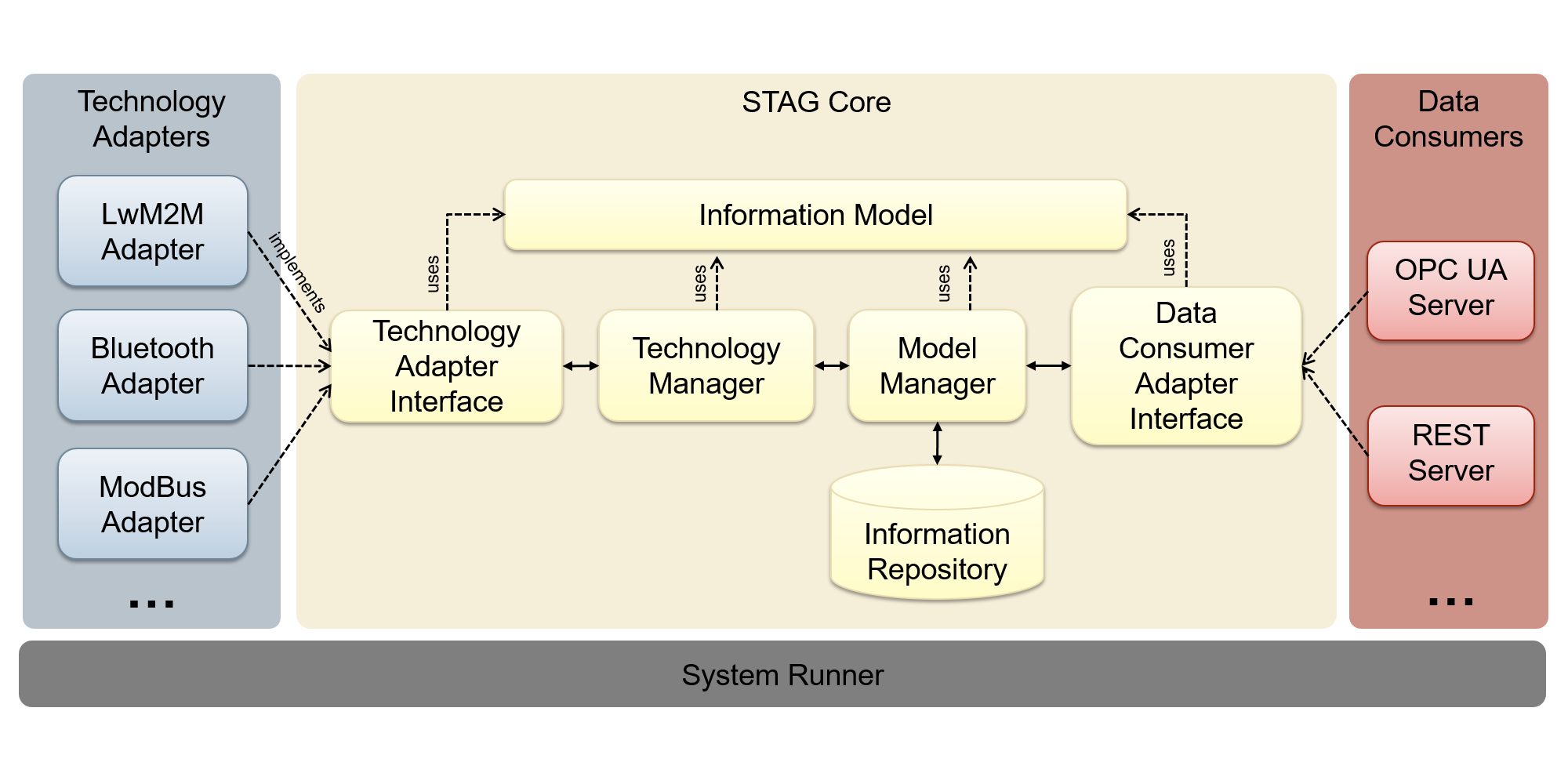
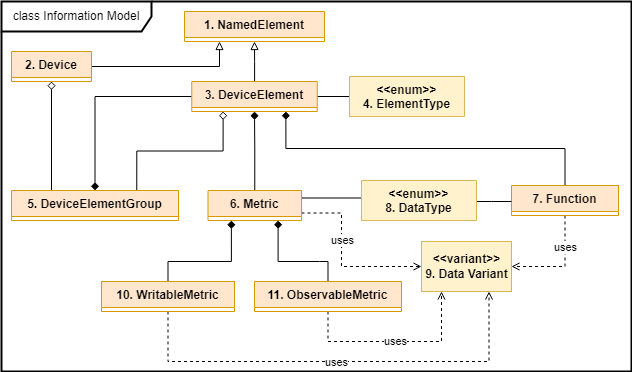
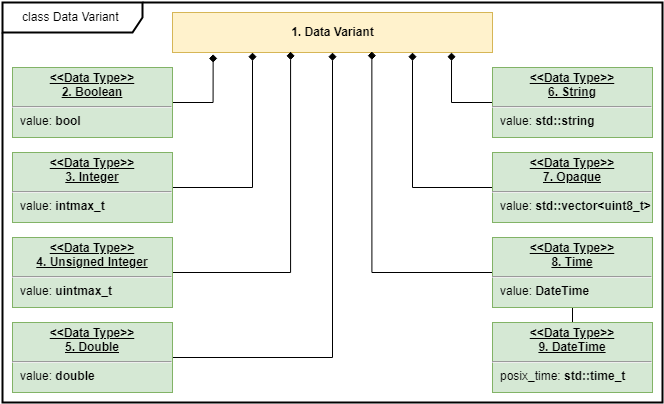
Split into three
STAG system is logically split into three main parts:
- Technology Adapter Implementation - various modules
that implement specific communication protocols that
create
Deviceabstractions for the internal information model. - Core - internal modules that provide the base functionality for the system as a whole.
- Data Consumer Adapter Implementations - various
modules that provide access to the internal information
model and the stored
Deviceabstractions.
Expandable at runtime
System administrators can add new Technology Adapter and Data Consumer Adapter Implementations without shutting down the system. The only part that is not expandable at runtime is the Core.